

Al Ta’leef Institute
The Al Ta’leef Institute was founded on the basis of enhancing the learning experience of the commun
Getting ready
- Understand the rituals of Hajj: Before embarking on the Hajj journey, it is important to have a good understanding of the rituals that will be performed during the pilgrimage. Muslims should study the Hajj rituals in detail, so they know what to expect and can perform the rituals correctly.
- Seek medical advice: Hajj involves a lot of walking, standing, and physical exertion, so it is essential to be in good health. Muslims should consult their doctor to ensure that they are physically fit to undertake the journey.
- Get vaccinated: Saudi Arabia requires all pilgrims to be vaccinated against certain diseases before entering the country for Hajj. Muslims should check with their doctor to ensure that they have received all the necessary vaccinations.
- Pack appropriately: Packing for Hajj requires careful planning. Muslims should pack comfortable, loose-fitting clothes that are appropriate for the hot climate of Saudi Arabia. They should also bring a small backpack to carry essentials like water, snacks, and medication.
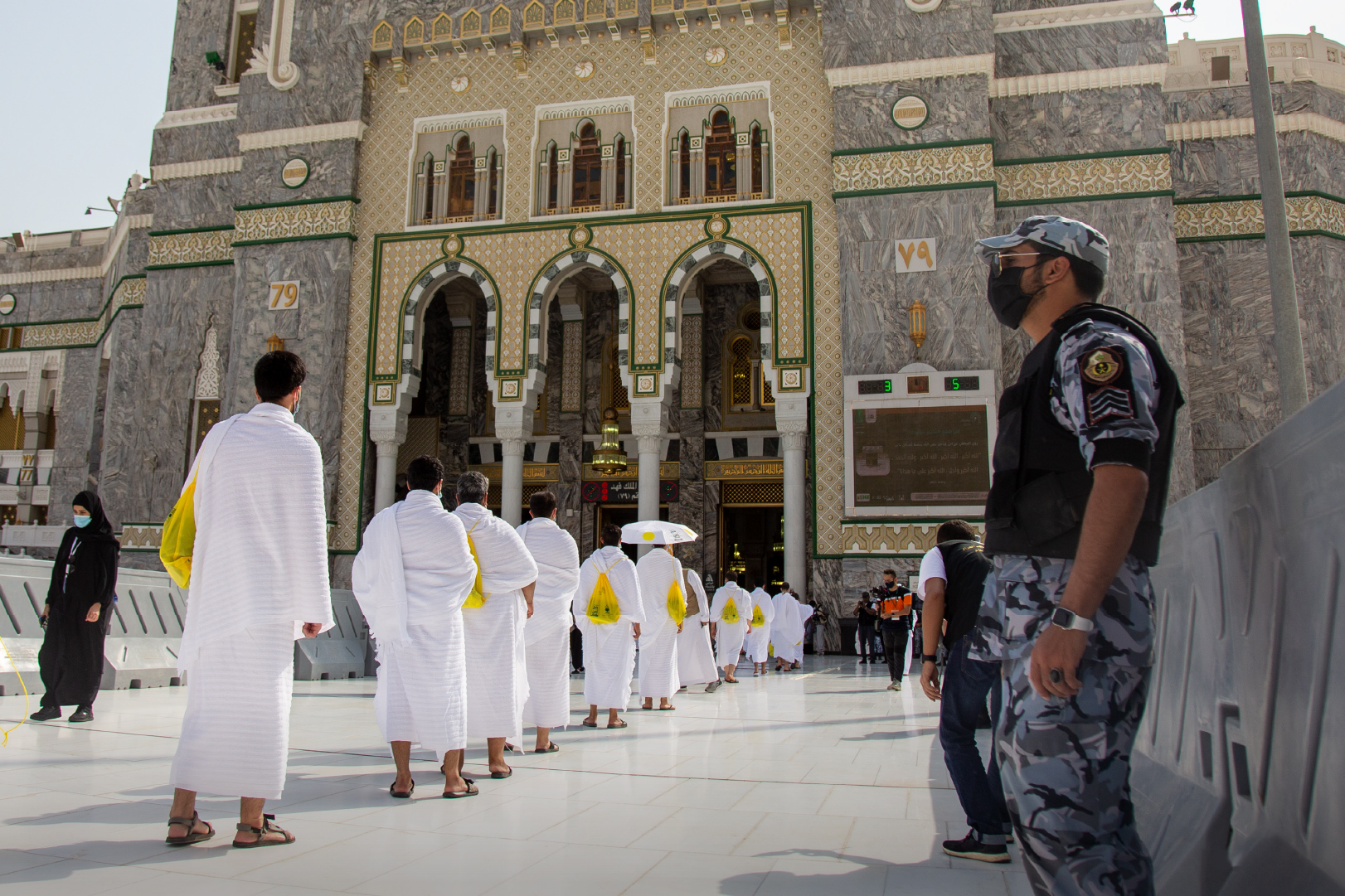


Registration
1.Eligibility: In order to register for Hajj, you must be a Muslim and meet certain eligibility requirements. You must be physically and financially able to perform the pilgrimage, as well as have a valid passport and visa to enter Saudi Arabia. Some countries may also require additional paperwork or health certificates, so it’s important to check with your local embassy or consulate for specific requirements.
2.Registration process: Hajj registration typically opens a few months before the start of the pilgrimage season. The Saudi Arabian government manages the registration process through an online portal, and applicants must create an account and provide their personal information, including their passport and visa details. Once you have completed the registration process, you will receive a confirmation email with your registration number.
3.Hajj packages: In addition to registering for Hajj, many pilgrims choose to purchase a Hajj package from a travel agency. These packages typically include transportation, accommodation, and other services to make the pilgrimage as comfortable and convenient as possible. When choosing a Hajj package, it’s important to research the travel agency carefully and read reviews from previous customers to ensure that you are getting a reputable and reliable service.
4.Payment: Hajj packages can be quite expensive, so it’s important to budget accordingly. When registering for Hajj, you will need to pay a registration fee, which varies depending on the country you are traveling from. In addition, if you choose to purchase a Hajj package, you will need to pay the full cost of the package upfront.
5. Deadlines: Hajj registration typically closes several weeks before the start of the pilgrimage season, so it’s important to register early to ensure that you secure a spot. Hajj packages can also sell out quickly, so it’s a good idea to book your package as soon as possible to avoid disappointment.
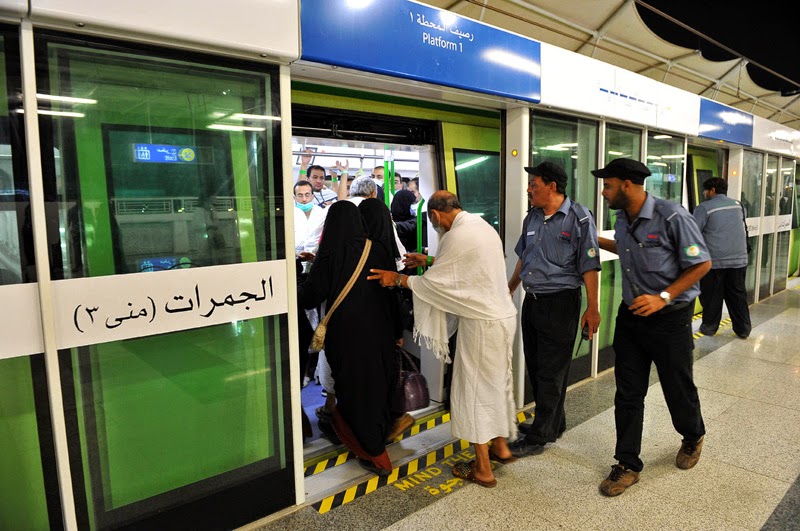
Routes
1.The journey begins in Makkah: The Hajj route begins in Makkah, where pilgrims perform the Tawaf, which is the circumambulation of the Kaaba, and the Sa’i, which is the running between the hills of Safa and Marwah. After completing these rituals, pilgrims put on their Ihram, which is the special clothing worn during the Hajj pilgrimage.
2.Moving to Mina: The next stop on the Hajj route is Mina, a small village located about 5 kilometers east of Makkah. Pilgrims spend the night in Mina, which serves as a staging area for the main events of Hajj.
3.Arafat: The most important part of the Hajj pilgrimage takes place on the plains of Arafat. Pilgrims spend the day in supplication and worship, seeking forgiveness and guidance from Allah. It is here that Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) gave his last sermon, which is considered one of the most important speeches in Islamic history.
4.Muzdalifah: After sunset, pilgrims move to Muzdalifah, where they spend the night sleeping under the open sky. This is also where they collect the pebbles that will be used for the stoning of the devil ritual.
5.Stoning of the devil: The next day, pilgrims return to Mina to perform the stoning of the devil ritual. This involves throwing pebbles at three pillars that represent the devil and his temptations.
6.Tawaf and Sa’i: After completing the stoning ritual, pilgrims return to Makkah to perform the Tawaf and Sa’i rituals again, marking the completion of the Hajj pilgrimage.
7.Eid-ul-Adha: The Hajj pilgrimage culminates with the celebration of Eid-ul-Adha, which is one of the most important festivals in the Islamic calendar. It is a time of joy and celebration, as well as reflection and gratitude for the blessings of Allah.

Health considerations
1.Vaccinations: All pilgrims are required to have certain vaccinations before they can enter Saudi Arabia. These vaccinations include meningitis, yellow fever, and polio. It’s important to consult with your doctor or local health authority to ensure that you have all the required vaccinations before you leave for Hajj.
2.Heat and dehydration: The Hajj pilgrimage takes place in the hot and dry climate of Saudi Arabia, and temperatures can reach up to 40 degrees Celsius. It’s important to drink plenty of water and other fluids to prevent dehydration, and to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun during the day.
3.Respiratory infections: Due to the large crowds of people who gather for Hajj, there is a risk of respiratory infections spreading. It’s important to practice good respiratory hygiene, such as covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and to avoid close contact with people who are sick.
4.Food and water safety: To prevent foodborne illnesses, it’s important to only eat food that has been cooked thoroughly and to avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat, poultry, or seafood. Additionally, it’s important to drink bottled water or water that has been boiled or treated with chlorine or iodine tablets to prevent waterborne illnesses.
5.Personal hygiene: Good personal hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of illnesses and diseases. It’s important to wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially before eating or preparing food, and to avoid sharing personal items such as towels or utensils with others.

